Difference between revisions of "DBA 2nd iteration Solution Architecture"
m |
|||
| Line 751: | Line 751: | ||
Error handling and logging. | Error handling and logging. | ||
|DR, DT | |DR, DT | ||
| − | |common | + | |common (MS deployment) |
|Needs extension for S&N and Lookup patterns to facilitate interaction on: | |Needs extension for S&N and Lookup patterns to facilitate interaction on: | ||
- subscriptions | - subscriptions | ||
| Line 760: | Line 760: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<span style="background:#FFFF00">Evidence service locator (ESL) configuration file Issuing Authority Locator (IAL) TBC</span> | |<span style="background:#FFFF00">Evidence service locator (ESL) configuration file Issuing Authority Locator (IAL) TBC</span> | ||
| − | |Change w.r.t. | + | |Configuration file for locating the service to reach out to. |
| + | |DR, DT | ||
| + | |common (MS deployment) | ||
| + | |Change w.r.t. iteration 1? There is no evidence provider lookup, instead the endpoint where to send the subscription request to is needed. Also there is no evidence response, it is event oriented now. | ||
| + | |||
As the DBA pilot’s MVP uses just one type subscription message with just one data provider per Member state (on NUTS0 level), there is no need for dynamic discovery of the data provider. For the DBA pilot it is sufficient to use a simple configuration file with the required elements (member state and participant id) like in iteration 1. | As the DBA pilot’s MVP uses just one type subscription message with just one data provider per Member state (on NUTS0 level), there is no need for dynamic discovery of the data provider. For the DBA pilot it is sufficient to use a simple configuration file with the required elements (member state and participant id) like in iteration 1. | ||
See logical interfaces section below | See logical interfaces section below | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SMP | ||
| + | |For each subscription request/response, information on the receivers Access Point (URL) and its certificates are needed. Each member state hosts an SMP for this purpose (note: for testing one single centrally hosted DE4A SMP will be used). Before sending a request or response, the sending party queries the SMP of the receiver to get this info. | ||
|DR, DT | |DR, DT | ||
| − | |common | + | |common (MS deployment) |
| − | | | + | |None expected. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |eDelivery AS4 gateway |
| − | | | + | |This component – also referred to as eDelivery access point – handles the secure transfer of the data, including encryption and decryption as well as signing/sealing and validating signatures/seals. |
|DR, DT | |DR, DT | ||
| − | | | + | |common (MS deployment) |
| − | | | + | |Needs configuration for accepting subscription, notifications and lookup messages for the second iteration. |
|- | |- | ||
|DNS & SML | |DNS & SML | ||
| Line 779: | Line 786: | ||
DNS entries will be created from the registration of SMP’s: the SML, which is also centrally hosted by CEF. | DNS entries will be created from the registration of SMP’s: the SML, which is also centrally hosted by CEF. | ||
|Central | |Central | ||
| − | |common | + | |common (centrally hosted by CEF) |
| − | | | + | |None expected. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Data Service | ||
| + | |The webservice of the data provider that will output the evidence requested. | ||
| + | |DO | ||
| + | |specific | ||
| + | |None expected. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Data source to OOP TS Interface | ||
| + | |Interface for connecting the data service with the OOP TS (IM & LKP). | ||
| + | |DO, DT | ||
| + | |specific | ||
| + | |None expected. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cross-border Event Handler | ||
| + | |Application component handling the cross-border events. It filters all domestic events for relevant cross-border events and takes care of preparing a notification message and compiling a subscribers list to which the notification must be sent. | ||
| + | |DO | ||
| + | |common (MS deployment) | ||
| + | |Needs to be developed and implemented by the DO. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Event handler to OOP TS Interface |
| − | | | + | |Interface for connecting the OOP TS with the Cross-border Event Handler. |
| − | | | + | |DO, DT |
| − | | | + | |specific |
| − | | | + | |Needs to be developed and implemented by the DT. |
|- | |- | ||
|Authorization Controller | |Authorization Controller | ||
|''In case of LKP'' | |''In case of LKP'' | ||
| − | + | Establish which data service / evidence types can be requested by the DE/MS and whether this is allowed under applicable Union or national law without user request and preview. This functionality prevents unauthorised lookup of evidences. | |
''In case of S&N'' | ''In case of S&N'' | ||
| − | + | Establishes whether the DE is allowed to subscribe. | |
| + | |||
| + | Established whether the DP is allowed to send a notification. This prevents unauthorised sending of (fake) notifications. TBD: do we need a common functionality for this or can we leave it up to the DE to check whether the notification comes from the authority to which it subscribed? | ||
|DR, DT | |DR, DT | ||
|common | |common | ||
| − | | | + | |To be developed. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Subscription System | |Subscription System | ||
|Application component managing the entire life cycle of subscriptions, i.e. creation and maintaining subscriptions. It also offers functionality for validating subscriptions (does subject exist?, is the event supported?, is the subscription changing an existing subscription?), confirmation of a subscription and error handling. | |Application component managing the entire life cycle of subscriptions, i.e. creation and maintaining subscriptions. It also offers functionality for validating subscriptions (does subject exist?, is the event supported?, is the subscription changing an existing subscription?), confirmation of a subscription and error handling. | ||
|DO | |DO | ||
| − | | | + | |common (MS deployment) |
| − | | | + | |To be developed |
|- | |- | ||
|Notification front-end | |Notification front-end | ||
|Application component providing the UI for civil servants to dispatch events and consult logging information for trouble shooting. | |Application component providing the UI for civil servants to dispatch events and consult logging information for trouble shooting. | ||
|DO | |DO | ||
| − | | | + | |common (MS deployment)? |
| − | | | + | |Out of scope for piloting DBA. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:20, 11 August 2021
DBA pilot iteration 2
The 2nd pilot iteration for DBA consists of:
- extending use of the intermediation pattern to allow for more fine grained powers validation (intermediation pattern remains unchanged, SEMPER extension will be added)
- the Subscription and notification pattern
- the Lookup pattern (the lookup of evidence, not individual attributes).
The solution architecture of (1) has been specified in chapter Solution architecture for DBA authentication and powers validation and the solution architecture for (2) and (3) have been included in chapter Solution architecture for Subscription & Notification pattern and Lookup pattern.
Solution architecture for DBA authentication and powers validation
This section contains the eIDAS solution architecture for the DBA pilot. eIDAS will be used for piloting the intermediation pattern in DBA pilot iteration 1 and 2.
In all DBA cases a natural person will represent a company in the cross-border eProcedure. In both iterations the powers of the representative will be validates. The granularity is different in both iterations though. In the first iteration only full powers will be validated. The pilot partners will use currently available eIDAS functionality for communicating this cross-borders. The second pilot iteration adds fine-grained powers validation to eIDAS. It allows for explicit expression of powers in a powers validation request and powers declaration. This requires extension of eIDAS with the SEMPER concepts and software.
General design decisions
The DBA eIDAS architecture has been designed according to the following general design decisions (see DBA deliverable D4.6):
- The DBA pilot will implement a pilot-eIDAS-network, meaning the Member States will implement dedicated pilot eIDAS nodes for cross-border authentication and powers validation that is isolated from the regular network of eIDAS nodes. As the project extends on the use of eIDAS with legal person attributes and powers validation, regular eIDAS nodes are not suitable for piloting. Furthermore, use of the dedicated eIDAS network allows for acceptance of non-notified eID for piloting only.
- The DBA pilot uses the eIDAS company identification attributes ('legal person attributes in eIDAS') to communicate the represented legal person to the DP. As most Member States do not provide these attributes currently, they need to be added for piloting.
- The DBA pilot will use eIDAS attribute profile 1.1 and/or CEF’s reference software for the eIDAS node version 2.4.
- The DBA pilot will use the SEMPER extension that is compatible with the eIDAS node 2.4 for fine-grained powers validation in the second pilot iteration.
Compared to current eIDAS practice, the use of eIDAS will be extended by the DBA pilot with:
- Requesting and sending legal person attributes (identifying the company that applies for the service). Although eIDAS has been able to send legal person attributes from the start, this functionality has been notified just twice (by IT and NL) and has not been used in production services.
- Validating powers of representation. This function is not part of the eIDAS-network currently.
Ad 1. Legal Person attributes & record matching at the DC
- The pilot partners will send the mandatory eIDAS attributes for the legal person after successful authenticating and validating powers (LegalPersonIdentifier and LegalName).
- The Data evaluator in the DBA pilot needs record matching on the company to determine whether the company has been registered at the company portal prior to the pilot start (without LegalpersonIdentifier). The data evaluator will use the second mandatory eIDAS attribute (LegalName) for that purpose. If needed the Data evaluator interacts with the user to do additional checks in the matching process. Record matching at the data evaluator is an eProcedure portal (or data consumer) specific activity that does not need harmonisation across piloting partners.
- The data owner does not need to do record matching on the company as it can use the LegalPersonIdentifier to uniquely identify the company involved. This is a consequence of the pilot principle, that the authenticating proxy sends an LegalPersonIdentifier containing a company identifier that the business register itself uses in its company registration.
- Data evaluators and data owners do not need to do record matching on the natural person. Therefore, no additional eIDAS attributes of the natural person are needed.
For more information, please see, please see DE4A D4.6 DBA Pilot Planning v1.0 final.pdf
Ad 2. Powers validation
- Pilot iteration 1 supports implicit full powers only. It uses the eIDAS network currently operational for sending the required information. The eIDAS infrastructure – from the start – supported exchange of natural person attributes as well as company identification attributes (‘legal person attributes’). The eIDAS regulation defined the minimum datasets for both the natural and the legal person. The eIDAS network lacks a possibility to specify the powers of representation though; attributes specifying the powers (‘the powers declaration’) have not been defined yet. Hence, in iteration 1 the pilot partners agreed on the following access policy rule: “In case of full powers, the eIDAS authentication will be successful and the authentication proxy sends the eIDAS legal person attributes as well. In case of insufficient powers, the authentication must fail at the eIDAS proxy.”. Only that way the data consumer knows whether the user has full powers or not.
- Pilot iteration 2 supports fine grained powers validation. By using the SEMPER extension on eIDAS, not only the natural and company identification attributes can be exchanged, an explicit powers declaration will be included as well. Using the extension, the data evaluator specifies the scope of the service the user needs powers for. After validating the powers, the authentication proxy constructs a powers declaration confirming or denying the person’s powers. This way, the extension allows for fine-grained powers validation.
Main design decisions regarding fine grained powers validation in iteration 2:
- the DBA pilot allows for representation of legal persons by natural persons only.
- the DBA pilot does not allow for intermediary parties (e.g. accounting firm operation on behalf of the company).
- the DBA pilot will operate a list of harmonised services to express the extent of powers. Non-harmonised services will not be supported.
- the DBA pilot will use the SDG annex II procedures as starting point for the list of harmonised services.
- the DBA pilot will implement fine grained powers using the SEMPER extension to eIDAS or implement the SEMPER concepts in custom eIDAS software.
For more information, please refer to DE4A D4.6 DBA Pilot Planning v1.0 final.pdf
Process realisation
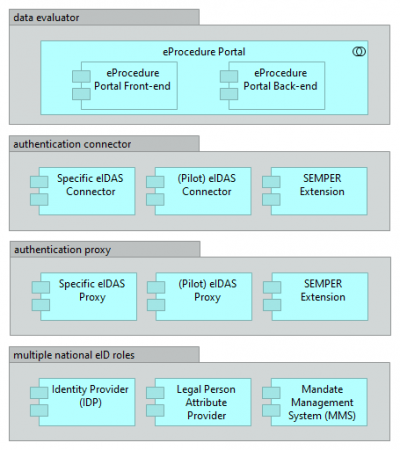
The table below presents the components that implement the application services for the DBA pilot.
| Process | Application service | Components |
| Request authentication, including powers validation | Authentication initiation | eProcedure portal |
| Specific eIDAS connector | ||
| eIDAS connector | ||
| SEMPER extension | ||
| Authenticate user | User authentication | Identity Provider |
| Validate powers of representation | User authentication | Mandate Management System |
| Retrieve legal person attributes | User authentication | Legal Person attribute provider (may be same as Mandate Management System) |
| Provide authentication details, including powers declaration | User authentication | Specific eIDAS proxy |
| eIDAS proxy | ||
| SEMPER extension |
check (Ivar) I've uploaded a new version of the image including eProcedure portal front-end. In edit mode it shows correctly. In read mode it shows the previous version of the image.
Component description
The table below describes each of the components in this solution architecture.
| Component | Short description of its use | Changes for 2nd iteration piloting |
| eProcedure portal | DC specific
The eProcedure portal handles all user interaction on the web. It connects to the national eIDAS node via the specific eIDAS connector. This requires the eProcedure portal to add the eIDAS login option to the login-webpage and interface to the specific eIDAS connector. As the DBA Pilot will use a dedicated network of eIDAS nodes, the eIDAS login option should be separated from the regular eIDAS login option (in case not already available on the eProcedure portal). The DBA login option should invoke the dedicated eIDAS connector instead of the regular one (a different URL). |
In iteration 1 the eProcedure portal should request:
In iteration 1 the eProcedure portal should apply the following rules for granting access after authentication:
In iteration 2 the eProcedure portal should request:
In iteration 2 the eProcedure portal should apply the following rules for granting access after authentication:
|
| Specific eIDAS connector | Member State Specific
The Member State specific component that translates national eID protocol into eIDAS (light) protocol for requesting authentication and powers validation. Member States usually implement one or more components to ‘bridge’ eIDAS to the national eID infrastructure. As from CEF eIDAS reference software 2.0, Member States use the eIDAS Light protocol for this. |
To enable fine grained powers validation in iteration 2, the specific eIDAS connector needs to be extended for requesting powers validation alongside authentication. |
| (pilot) eIDAS connector | Common component (MS deployment)
The component Member States implement to connect to the eIDAS network as a relying party. The connector accepts authentication requests from the data evaluators of the Member State and forwards the requests to the Member States that needs to authenticate the user. After authentication, the eIDAS connector receives the authentication results and sends them to the requesting data evaluator. The eIDAS connector can be implemented using CEF’s reference software or a custom implementation compliant to the eIDAS interoperability specifications. The CEF reference software implements – besides the eIDAS SAML profile – also the JSON/REST eIDAS Light protocol to connect to national infrastructure. |
No changes in 2nd pilot iteration. |
| SEMPER extension | Common component (MS deploymentt)
Component for extending the eIDAS connector and the eIDAS proxy to allow for explicit powers validation requests and powers declarations. |
Needs to be deployed by Member States for communicating fine grained powers in iteration 2.
This component has been developed by the SEMPER project and needs to be deployed on the eIDAS node of each of the Member States. As an alternative Member States May develop a custom implementation of the SEMPER software that complies with the SEMPER SAML interface specifications. |
| (pilot) eIDAS proxy | Common component (MS deployment)
The component Member States implement to allow authentication with their (notified) eID for services provided in other Member States. The eIDAS proxy receives authentication requests from relying Member States, coordinates authentication, retrieval of legal person attributes and powers validation. The eIDAS proxy then sends the result to the requesting eIDAS connector. Just like the eIDAS connector, the eIDAS proxy can be implemented using CEF’s reference software or a custom implementation compliant to the eIDAS interoperability specifications. The CEF reference software implements – besides the eIDAS SAML profile – also the JSON/REST eIDAS Light protocol to connect to national infrastructure. |
No changes in 2nd pilot iteration. |
| Specific eIDAS proxy | Member State Specific
The Member State specific component that translates national eID protocol into eIDAS (light) protocol for performing authentication and powers validation. Member States usually implement one or more components to ‘bridge’ eIDAS to the national eID infrastructure. As from CEF eIDAS reference software 2.0, Member States use the eIDAS Light protocol for this. Furthermore, the eIDAS proxy coordinates the login process at the DP Member State by triggering the IdP, Legal Person AP and MMS. |
In the second pilot iteration the Specific eIDAS proxy needs to be adapted to translate the powers validation request (the scope of powers to be precise) to national powers taxonomy, send a powers validation request to the Mandate Management System in national protocol, receive and interpret the response from the Mandate Management System and translate it back to cross-border taxonomy. |
| Identity Provider | Member State Specific
The Identity Provider handles authentication of the natural person. The IdP may be notified under eIDAS, but does not need to be notified to be used in the DBA pilot. |
No changes in 2nd pilot iteration. |
| Legal Person AP | Member State Specific
Member States need to provide the identifying (mandatory) attributes of the legal person (eIDASLegalPersonID and eIDASLegalName) to the specific eIDAS proxy. Member States could provide optional attributes of the legal person. The Legal Person attributes may be integrated in the national eID scheme. For example, in eRecognition (NL) the mandate management system also provides the legal person attributes. Mandate Management System and Legal Person AP are one and the same component then. |
No changes in 2nd pilot iteration. |
| Mandate Management System | Member State Specific
Member State specific solutions for registration and validation of powers. |
In the DBA first pilot iteration, this source must be used to verify full powers . The declaration of powers that results from validating full powers is implicit: in case the authentication is successful, the user will have full powers to represent the company.
In the second pilot iteration, when using SEMPER, the powers declaration is explicit: the powers declaration relates to the requested powers declaration and can be a powers declaration for a specific eService as well as a (explicit) powers declaration for full powers. Optionally (depending on national implementation) the harmonised services need to be included in the MMS. |
Functional requirements
The table below presents the requirements that the data evaluator and the authentication connector must implement.
| Role | Component | requirement |
Use in pilot iteration 1 |
use in pilot iteration 2 |
| Data evaluator | eProcedure portal | The eProcedure portal adds an eIDAS login option for piloting. | x | x |
| The eProcedure portal connects to a dedicated eIDAS pilot node. | x | x | ||
| The eProcedure portal requests eIDAS legal person attributes (mandatory ones) | x | x | ||
| The eProcedure portal grants the user access on behalf of the company in case of an “authentication successful” response. | x | |||
| The eProcedure portal additionally constructs a fine-grained powers validation request. | x | |||
| The eProcedure portal validates the Powers declaration received. | x | |||
| Authentication connector | SEMPER extension | MS implements SEMPER extension to the eIDAS connector. | x | |
| Specific eIDAS connector | MS adapts the "specific eIDAS connector" to support powers validation requests and powers declarations | x | ||
| eIDAS connector | MS implements eIDAS connector 2.4. In case of a custom implementation (like Sweden) an attribute profile 1.1-compliant version of the connector will be used for piloting. | x | x | |
| Authentication proxy | SEMPER extension | MS implements SEMPER extension to the eIDAS proxy. | x | |
| Specific eIDAS proxy | MS adapts the "specific eIDAS proxy" to support powers validation requests and powers declarations | x | ||
| eIDAS proxy | MS implements CEF eIDAS proxy 2.4.
In case of a custom implementation (like Sweden) an attribute profile 1.1-compliant version of the connector will be used for piloting. |
x | x | |
| Ms connects an IdP to the eIDAS proxy node for authenticating the natural person | x | x | ||
| MS connects attribute provider (AP) to eIDAS node for eIDAS legal person attributes (in case not integrated in the MMS) | x | x | ||
| MS connects mandate management system (MMS) to eIDAS node for validating powers. Note: AP and MMS could be the same data source. | x | x | ||
| Ms validates full powers | x | |||
| MS adds fine-grained powers validation | x |
Component Deployment
The table below shows the required deployment of common components.
| Component | Version |
|---|---|
| eIDAS connector | CEF reference software version 2.4
or custom software implementing interoperability specs 1.1 |
| eIDAS proxy | CEF reference software version 2.4
or custom software implementing interoperability specs 1.1 |
| SEMPER extension | The 2.4-compliant version of the SEMPER extension provided by Technical University Graz (SEMPER project) |
Open questions AT:
- can we upgrade to eIDAS node 2.5? No compatible SEMPER extension available (check with TUG).
- can we adapt the way we request attributes for iteration 1? -> don't request the natural person attributes, use the natural person representative attributes for this (profile 1.2 style).
Configuration of authentication requests
Configuration for pilot iteration 1
- regular eIDAS request & response
- eIDAS attributes to request: natural person and legal person attributes (at least the mandatory ones)
- eIDAS attributes to respond with: natural person and legal person attributes (at least the mandatory ones) - including a copy of natural person attributes as representative is optional.
Configuration for pilot iteration 2
- regular eIDAS request & response
- eIDAS attributes to request: legal person attributes only (at least the mandatory ones)
- eIDAS attributes to respond with:legal person attributes (at least the mandatory ones) and representative natural person attributes (at least he mandatory ones) using the representative-prefix
- powers validation request & powers declaration (response)
- request:
- scope of powers to validate
- type of representation allowed
- source of powers accepted
- response:
- validation result (successful or not)
- type of representation
- source of powers
- request:
Configuration of harmonised services
Principles for configuration:
- The DBA pilot will rely on a common library of services to express the extent of powers: the harmonised services. This way, each of the participating Member States understand the powers validation requests of other Member States. It's up to each of the Member States to translate the harmonised services into nationally defined services (authentication connector-side) / powers (authentication proxy-side).
- The DBA pilot will use the SDGR services as starting point. These services have been defined in European legislation (as procedures in annex II of the Regulation). Hence, they have been pre-defined and harmonised already across Europe. The DBA pilot defines the "SDGR" harmonised services catalogue for use in the SEMPER extension.
- The DBA pilot is not limited to SDGR services though, e.g. opening a branch cross-border is explicitly excluded from the SDGR, but is included in some of the pilot scenario's. For services 'beyond SDGR' the DBA pilot has defined the "SDGR+" harmonised services catalogue.
Proposal for the harmonised services to express powers cross-border:
| Service catalogue | Nr | Harmonised service |
|---|---|---|
| SDGR | 1 | Notification of business activity, permission for exercising a business activity, changes of business activity and the termination of a business activity not involving insolvency or liquidation procedures |
| SDGR | 2 | Registration of an employer (a natural person) with compulsory pension and insurance schemes |
| SDGR | 3 | Registration of employees with compulsory pension and insurance schemes |
| SDGR | 4 | Submitting a corporate tax declaration |
| SDGR | 5 | Notification to the social security schemes of the end of contract with an employee, excluding procedures for the collective termination of employee contracts |
| SDGR | 6 | Payment of social contributions for employees |
| SDGR+ | 1 | Starting of a company or opening as branch |
| SDGR+ | 2 | Initial registration of a business activity with the business register |
Logical interfaces
SAML interface specifications for regular authentication requests (pilot iteration 1) have been specified by CEF Digital: https://ec.europa.eu/cefdigital/wiki/display/CEFDIGITAL/eIDAS+eID+Profile SAML interfaces specification for SEMPER-extended authentication request and response (pilot iteration 2) have been specified by SEMPER: see chapter 6 from deliverable M3 Report on mandate attributes and solutions for cross-border mandate attributes - 1.0.
Solution architecture for Subscription & Notification pattern and Lookup pattern
This section specifies the solution for the two additional patterns that will be piloted by the DBA pilot in the second iteration: the Subscription & notification pattern and the Lookup pattern.
- Within scope
- Modify DO/DE Mocks for S&N en Lookup patterns: for testing the new patterns, new versions of the DO- and DE-mocks need to be developed by WP5.
- Common component for Cross-border subscriptions and notification (optional for MS to use, i.e. not mandatory).
- Event Notification + Evidence Lookup, in line with PSA 2nd iteration: the PSA defines several options for implementing the S&N pattern. The option chosen provides a solution for notifying business events and triggering of the Lookup pattern in case (an updated version of) evidence is required by the DE.
- Outside scope
- Resend a subscription request in case of an error: instead the possibility to inspect the logs and manually resend a request is deemed sufficient for piloting.
- Include the Evidence in the notification: in case the DE needs (an updates version of) the evidence, it will use the Lookup pattern.
- Attribute Lookup: this solution architecture support Evidence type lookup requesting the full evidence without user interaction. The option to request individual attributes / API-approach is not supported.
Prerequisite from the DE4A-project is the use of eDelivery and AS4 for the exchange of messages in the S&N and Lookup patterns. This means that eDelivery will be used for:
- requesting a subscription (DE to DO)
- confirming a subscription (DO to DE)
- notifying a business event (DO to DE)
- requesting evidence (DE to DO)
- sending the evidence (DO to DE)
In the next sections the general design decisions, process realisations, component descriptions, requirements, component implementations and expected logical interfaces are described.
General Design Decisions
- The OOP TS domain (WP5) provide the data requestor and data transferor with the components needed for:
- exchange of cross-border subscription and notification messages
- performing the lookup of an evidence
- The DBA pilot uses one type of subscription message and one type of notification message that all DC’s and DP’s involved will use. The subscription message is for subscribing to cross-border events generated at the DP. The notification message is for notifying the DC of such events. If the DC desires the Evidence can be retrieved using the Lookup. This implies an update of the IEM (WP3).
- There will be just one data provider per Member state: the business register, where the subscription will be recorded and where the cross-border events are generated, i.e.is the authentic source of company information. The pilot does not support multiple DO's / notifying authorities in one Member State.
- The DC will subscribe in one Member State at a time.
- The DP will notify one Member State at the time. In case DE's from different Member States have subscribed to business events of a single company, the DP needs to notify each of the Member States individually.
- The explicit request and the preview functions won't be implemented, in both interaction patterns there is no user involvement. Please note that business event notification is considered an extension to the SDGR.
Process realisation
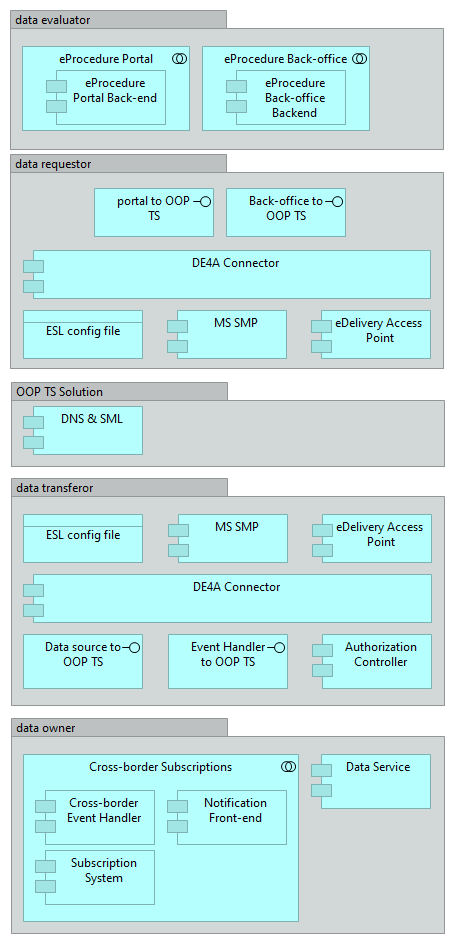
The solution for the OOP TS chain consists of required functionality of the OOP Technical System expressed as application components and interfaces in the diagram below. Some OOP TS components need to be implemented by the data requestor and data transferor, some components by the data evaluator and data owner and some are common components to be implemented by DE4A WP5. The image below depicts the solution with the familiar split in the different roles. It is a consolidated view of the Intermediation pattern, Subscription & Notification pattern (S&N) and Lookup pattern (LKP).
The table below presents the components that implement the application services for the DBA pilot. The process realisation is dealt with per pattern with S&N split in two (subscription and notification) as they are independently triggered. See Subscription and Notification Pattern and Lookup Pattern for more details.
The process realisation for the intermediation pattern has been specified in the solution architecture for the first pilot iteration already (not included on this page).
Subscription
| Process | Application Service | Components |
| Initiate subscription (DC) | Subscription Initiation | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Change subscription (DC) | Subscription Initiation | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Lookup event provider routing information (DC) | Inquire Routing Information | Data Service Lookup |
| Send subscription request (DC) |
|
|
| Validate subscription request (DP) |
|
|
| Evaluate subscription request (DP) | Subscription Evaluation | Subscription System |
| Exception: Prepare subscription error message (DP) | Subscription Error Handling | Subscription System |
| Exception Send subscription error message (DP) |
|
|
| Exception: Forward subscription error (DC) | n/a | |
| Exception: Investigate reason for subscription error (DC) | n/a | |
| Register subscription (DP) | Subscription Creation and Update | Subscription System |
| Confirm subscription (DP) | Subscription Confirmation | Subscription System |
| Send subscription confirmation (DP) |
|
|
| Forward confirmation (DC) | n/a | |
| Log subscription information (DC) | n/a |
Notification
| Process | Application Service | Components |
| Identify event (DP) | Cross-border Event Filter | Cross-border Event Handler |
| Check subscriptions (DP) | Subscription Lookup | Subscription System |
| Prepare notification message and subscriber list (DP) | Notification Message and Subscriber List Preparation | Cross-border Event Handler |
| Exception: Resend past events (DP) | Manual Event Dispatch | Notification Front-end |
| Resolve service metadata (DP) | Inquire Routing Information | Data Service Lookup |
| Exception: Resolve subscriber participant ID and inform National Contact Point (DP) | Subscription Mismatch Log | Notification Front-end |
| Send event notification (DP) |
|
|
| Validate event notification (DC) |
|
|
| Determine event response (DC) | Event Evaluation | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Request change of subscription (DC) |
|
eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Dismiss event (DC) | Update Notification Response Log | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Trigger evidence lookup (DC) | Update Notification Response Log | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
| Notify Responsible Organization (DC) | Update Notification Response Log | eProcedure Back-office Backend |
Lookup
Note: compared with Intermediation the user is absent.
| Process | Application Service | Component |
| Determine required cross-border evidence (DC) | Cross-border Evidence Matching | Evidence Type Translator |
| Lookup routing information (DC) | Inquire Routing Information | Data Service Lookup |
| Request evidence (DC) |
|
|
| Evaluate evidence request (DP) |
|
|
| Establish subject identity (DP) | Identity/Record Matching | Record Matching
(needed for company matching right?) |
| Communicate non-availability of OOP (DP) |
|
|
| Extract evidence (DP) | Evidence Lookup | Evidence Query |
| Communicate non-availability or Delay of evidence (DP) |
|
|
| Establish non-availability of OOP (DC) | Evidence Request Tracker | Evidence Interchange Back-end |
| Compose evidence response (DP) | Domestic to Cannonical Evidence Transformation | Evidence Portal Back-end |
| Transfer evidence (DP) |
|
|
| Forward evidence (DC) |
|
|
| Evaluate evidence (DC) | Requirements/Evidence Matching | eProcedure Rules Engine |
Component description
The following table lists the components indicated in the image above. Per component a short decription of its use is given, by which role the component is used (i.e. DE, RDR, DT, DP) and whether the component is MS specific or common functionality.
| Component | Short description of its use | Role | Genericness | Changes for 2nd iteration piloting |
| eProcedure Portal Back-end | The eProcedure back-end handles all eProcedure specific logic. | DE | specific | For the S&N pattern this logic might need to be adapted to include rules for informing the user on subscriptions & possibly notifications. |
| Portal to OOP TS Interface | Member states may (but do not need to) implement an interface from national OOP protocols to the DE4A data model (DE4A connector). Such an interface guarantees that the data evaluator/owner can use the same (national) OOP protocols and services for cross-border use as well. | DE, DR | specific | None.
This interface is used for the intermediation pattern (subscriptions and notifications will be triggered from the eProcedure backoffice) |
| eProcedure Back-office Backend | This component implements back-end functionality for executing the eProcedure. Examples in the context of S&N:
|
DE | TBD | TBD is the required functionality is generic enough to justify a common component? Each DE needs to keep track of its subscriptions and needs some event handling as well. |
| Back-office to OOP TS | Interface for connecting the DE's backoffice with the OOP TS for:
Just like the portal to OOP TS interface, Member States may choose to implement this interface in a generic way to bridge national OOP protocols to DE4A datamodel at one single place. Furthermore, Member States may choose to integrate both interfaces (portal to OOP TS and backoffice to OOP TS) in one single interface. |
DE, DR | specific | Needs to be developed and implemented for the second iteration.
May be partial re-use of the portal-to-OOP interface. |
| DE4A Connector | Taking care of eDelivery and IDK interfacing, shielding DR and DT from complexities and facilitating ease of implementation.
Error handling and logging. |
DR, DT | common (MS deployment) | Needs extension for S&N and Lookup patterns to facilitate interaction on:
- subscriptions - notifications - evidences (Lookup style). |
| Evidence service locator (ESL) configuration file Issuing Authority Locator (IAL) TBC | Configuration file for locating the service to reach out to. | DR, DT | common (MS deployment) | Change w.r.t. iteration 1? There is no evidence provider lookup, instead the endpoint where to send the subscription request to is needed. Also there is no evidence response, it is event oriented now.
As the DBA pilot’s MVP uses just one type subscription message with just one data provider per Member state (on NUTS0 level), there is no need for dynamic discovery of the data provider. For the DBA pilot it is sufficient to use a simple configuration file with the required elements (member state and participant id) like in iteration 1. See logical interfaces section below |
| SMP | For each subscription request/response, information on the receivers Access Point (URL) and its certificates are needed. Each member state hosts an SMP for this purpose (note: for testing one single centrally hosted DE4A SMP will be used). Before sending a request or response, the sending party queries the SMP of the receiver to get this info. | DR, DT | common (MS deployment) | None expected. |
| eDelivery AS4 gateway | This component – also referred to as eDelivery access point – handles the secure transfer of the data, including encryption and decryption as well as signing/sealing and validating signatures/seals. | DR, DT | common (MS deployment) | Needs configuration for accepting subscription, notifications and lookup messages for the second iteration. |
| DNS & SML | As there are multiple SMP’s, the sending party needs to know where to find the SMP of the receiver to get the actual metadata. This location can be found in the centrally CEF-hosted DNS, that will be queried by the access point of the sending member state.
DNS entries will be created from the registration of SMP’s: the SML, which is also centrally hosted by CEF. |
Central | common (centrally hosted by CEF) | None expected. |
| Data Service | The webservice of the data provider that will output the evidence requested. | DO | specific | None expected. |
| Data source to OOP TS Interface | Interface for connecting the data service with the OOP TS (IM & LKP). | DO, DT | specific | None expected. |
| Cross-border Event Handler | Application component handling the cross-border events. It filters all domestic events for relevant cross-border events and takes care of preparing a notification message and compiling a subscribers list to which the notification must be sent. | DO | common (MS deployment) | Needs to be developed and implemented by the DO. |
| Event handler to OOP TS Interface | Interface for connecting the OOP TS with the Cross-border Event Handler. | DO, DT | specific | Needs to be developed and implemented by the DT. |
| Authorization Controller | In case of LKP
Establish which data service / evidence types can be requested by the DE/MS and whether this is allowed under applicable Union or national law without user request and preview. This functionality prevents unauthorised lookup of evidences. In case of S&N Establishes whether the DE is allowed to subscribe. Established whether the DP is allowed to send a notification. This prevents unauthorised sending of (fake) notifications. TBD: do we need a common functionality for this or can we leave it up to the DE to check whether the notification comes from the authority to which it subscribed? |
DR, DT | common | To be developed. |
| Subscription System | Application component managing the entire life cycle of subscriptions, i.e. creation and maintaining subscriptions. It also offers functionality for validating subscriptions (does subject exist?, is the event supported?, is the subscription changing an existing subscription?), confirmation of a subscription and error handling. | DO | common (MS deployment) | To be developed |
| Notification front-end | Application component providing the UI for civil servants to dispatch events and consult logging information for trouble shooting. | DO | common (MS deployment)? | Out of scope for piloting DBA. |
Functional requirements
For DBA the Authorization Controller needs to check that only parties in the pilot send subscriptions and notifications.
In case of the lookup pattern (and possibler IM) the Authorization Controller checks if the vidence may be requested by DE.
The "list" from the service Notification Message and Subscriber List Preparation can be restricted to one party only.
For technical error messsages the existing WP5 list can be used. Business error messages in case of S&N TBD. For the pilot it is probably sufficient to establish the notification was received by DR (DT->DR).
Business error messages:
- DO: subscription registration failed
- DO: suscription change failed
Cross-border Event Handler
Subscription System: Registering the subscription at DP and logging subscription at DC is similar in functionality but mirrored. This could be common component (reference implementation) or at least a specification. This component would be optional for MS to use. TODO data model, operations, logical I/Fs.
A DC subscribes to the full set of cross-border events (the set is TBD).
There are two types of events, those that trigger an evidence update and those that don't. DBA needs support for a small set (5-6) of events containing both event types.
The Cross-border Event Handler could maybe be part of the Connector or at least be a common component. All DPs need this functionality.
The table below presents the requirements that the actors involved need to implement.
TO DO: check alignment of table and PSA 2nd iteration.
| Role | Nr | DBA requirement | Comment |
| Data evaluator | 1 | The DE should be able to subscribe to the combination of:
|
For piloting it is sufficient to skipp the specification of events to subscribe to. It will be all or none. |
| 2 | The DE should monitor actual subscription at the DO by processing the subscription confirmation / error. | ||
| 3 | The DE should have the option to set a defined time frame for receiving notifications to automatically end a subscription. | ||
| 4 | The DE should be able to manage the “end date” of the subscription (prolong, shorten, …). | ||
| 5 | The DE should be able to unsubscribe to all notifications for a company at once. | See req 1. for piloting a "all or none" subscription is fine. | |
| 6 | The DE should at any time have an overview of all its subscriptions in order to manage them. | ||
| 7 | The DE may process a notification instantly, but may also choose to process the notifications in batch, e.g. once a day or week. | ||
| 8 | The DE should have a legal basis for processing business events. | It’s up to the DE to manage this. The DE will be accountable for its data processing. | |
| Data requestor | 1 | The DR must confirm having received the notification (by the DR not the DE) to the DT. | From that point on delivery of the notifications to the DE is the responsibility of the DR (and not the DT or DO). |
| 2 | The DR should provide a facility for delayed forwarding of notifications to the DE. | The probably needs a queue for this. This queue should guarantee delivery of the notifications to the DE, even if the DE is not online at some point in time. | |
| Data transferor | 1 | The DT needs to confirm having received the subscription request to the DR. | |
| Data owner | 1 | The DO should send a confirmation of (un)subscription to the DE. | Including error code and handling. |
| 2 | The DO should send notifications only for a business event occurring to a company for which the DE has subscribed – for as long as the subscription is valid. | ||
| 3 | The DO should include the company identifier in the notification to allow the DE to find the corresponding record in its registry. | ||
| 4 | The DO should include additional company identifiers that the business event concern. | E.g. The identifiers of the company / companies acquiring the company concerned. | |
| 5 | The DO should clearly state in the notification what business event has occurred. | ||
| 6 | The DO should provide a timestamp of the business event separate from the timestamp of the notification. | ||
| 7 | The DO may send notifications instantly, but may also send in batch, e.g. once a day or week. | ||
| 8 | The DO should be able to send notifications independently of the availability of the DE. | In order not to hinder the notification process of the DO. | |
| 9 | The DO should not include any additional company data in the notification nor attach evidence of any type to the notification. | Data minimisation.
It will be up to the DE to process the notification. This might not need any additional data. | |
| 10 | The DO should implement one event for notifying "the company registration evidence has changes" (without specifying which business event has occurred - if any). | To cover for data changes that might be relevant for the DE without begin a direct consequence of the occurrence of a harmonised business event, e.g. e-mail address changed. |
Component deployment
DNS, SML will be reused from iteration 1.
The Evidence service locator (ESL) configuration file probably needs to change. TBD
SMP, eDelivery AS4 gateway will be reused from iteration 1.
The DE4A Connector needs an update.
Various MS specific interfaces may be needed for (sub)system integration.
Both DE and DO need to do bookkeeping of subscriptions.
Both DE and DO need some sort of event handling.
Configuration of business events
List of harmonised events in the Event catalogue "Business events" (to support by the DBA pilot):
- Company ended its operations
- Company changed its legal form
- Company merger or takeover
- Company moved to another location
- Company administration changed
- Company registration evidence has changed
TO DO: validate within DBA pilot.
National-to-harmonised translation needs to be designed by each Member State. Example for NL below (concept).
| nr | harmonised event | NL event equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Company ended its operations | beëindigen rechtspersoon
opheffen onderneming |
| 2 | Company changed its legal form | omzetten rechtspersoon |
| 3 | Company merger or takeover | fuseren rechtspersoon |
| 4 | Company moved to another location | verhuizen vestiging |
| 5 | Company administration changed | toetreden bestuurder
toetreden functionaris toetreden gemachtigde toetreden aansprakelijke bij samenwerkingsverband uittreden functionaris/bestuurder/gemachtigde/aansprakelijke bij samenwerkingsverband |
| 6 | Company registration evidence has changed | (not an event) |
Logical interfaces
The expected logical interfaces are expected to remain largely the same with an expansion for the new patterns.
We need to discuss with WP3/WP5 the implementation of the Data Service Lookup ABB. Right now this is covered by two SBBs ESL and IAL.However, for S&N there is no evidencen lookup or exchange, so at least the name is off. Also the I/F with the Connector changes slightly. In the table below some differences are indicated.
| Component | Expected interface |
| Evidence service locator (ESL) configuration file Issuing Authority Locator (IAL) TBC | IN (from DE4A connector to ESL configuration file):
- Member state - event type (e.g.DBA = business event) OUT from ESL configuration file to DE4A connector): - participant ID |
| SMP | IN (from DE4A connector to SMP):
- Participant ID OUT (from SMP to DE4A connector): - Service URL - Certificate to use |
| DNS & SML | IN (from DE4A connector to DNS):
- Member state - Participant ID OUT (from DNS to DE4A connector): - SMP location |
| eDelivery AS4 gateway | IN (from DE4A connector to eDelivery AS4 gateway):
- subscription request/notification OUT (from eDelivery AS4 gateway to DE4A connector): - ACK |
| DE4A Connector | subscription
Initiating or changing subscription IN (from data evaluator to DE4A connector): - request ID (correlation) - subject identifier (company in question) - data owner identifier (DO id = participant ID) - subscriber identifier (DE id = participant ID) - event catalogue (DBA fixed business events) - action 'subscribe'/'change subscription' - (new) subscription start and end date OUT (from DE4A connector to DE): - ACK (from DT) subscription confirmation DO -> DE IN - request ID - data owner identifier (DO id = participant ID) - subscriber identifier (DE id = participant ID) - status (success/fail) OUT - ACK
notification IN (from data provider to DE4A connector): - subscriber identifier (DE ID = participant ID) - data owner identifier (DO id = participant ID) - Notification 1. catalogue event 2. event 3. timestamp event OUT (from DE4A connector to DR): - ACK (from DR)
lookup As in iteration 1. |
| Authorization Controller | lookup
IN - DE id = participant ID - evidence type id
- yes/no
IN - data evaluator identifier (DE id = participant ID) - event catalogue
- yes/no |
| Cross-border Event Handler | IN
- domestic event
- cross-border event or n/a |
| ... |
Appendix: archimate component diagrams
Solution architecture for DBA authentication and powers validation
Solution architecture for Subscription & Notification pattern and Lookup pattern
TODO merge AC's and tailot to MVP.