Difference between revisions of "DE4A Connector it2"
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
* Error sending message to Data Requestor via AS4 gateway - RequestId: <code>{0}</code> | * Error sending message to Data Requestor via AS4 gateway - RequestId: <code>{0}</code> | ||
* Data Owner address not found - DataOwnerId: <code>{0}</code> | * Data Owner address not found - DataOwnerId: <code>{0}</code> | ||
| + | [1] The <code>{x}</code> symbols are placeholders for dynamic text to be logged. | ||
Revision as of 09:29, 10 November 2022
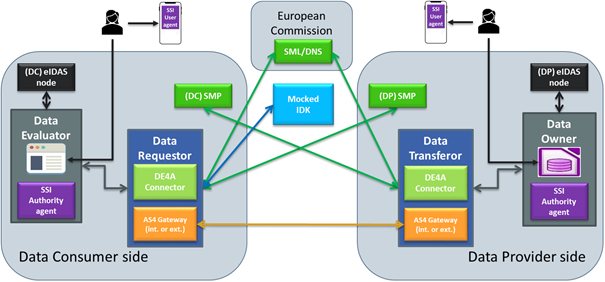
The DE4A Connector is a technical proxy that allows the final participants (DE or DO) to send requests for evidence or responses to other final participants over an eDelivery communication environment. In addition, to handle the message exchange process, the Connector is responsible for obtaining the message routing information, by exchanging information with external components such as the IDK, the SML/DNS or the SMP.
To do so, it provides a common interface to DEs and DOs, making the complexity of the system transparent to the final participants and integration easier.
The Connector component provides the AS4 Gateway functionality, so it can assume both the role of Data Requestor and Data Transferor. This first approach makes the Connector a stand-alone web application that can be deployed on any suitable application server.
The security and integrity of messages, as well as the unique identification of the participants involved, are the cornerstones of the Connector component.
Follow the link to the Installation and configuration guide of the DE4a Connector.
Functionalities provided
The main purpose of the DE4A Connector is sending and receiving of evidence requests and their responses. The message exchange process is described in the DE4A deliverables D2.4 Project Start Architecture and D5.3 Initial technical design of interfaces.
Routing information lookup
The Connector is responsible for obtaining the Data Provider information from the IDK. It exposes a REST API /lookupRoutingInformation to get information about the Data Owners that provide a specific Canonical Evidence Type and further related information. That information is used to construct a request message to be sent through the Connector. Thus, the Data Evaluator is the only consumer of the mentioned API method.
Dynamic discovery of Services
In order for the Connector to be able to send a message to the corresponding endpoint, the eDelivery dynamic discovery mode of operation is used. This operation mode is based on the use of the IAL and SML/DNS and SMP components of the eDelivery infrastructure.
The IAL is a new component for it2, it offers centralized information of all the SMPs deployed at each partner infrastucture. When a request is performed to the IAL it gathers the distributed information en each SMP to enroute to the correct destination.
The main elements stored in the SML/DNS and SMPs for this purpose are the following:
- ParticipantIdentifier: The Data Owner/Data Evaluator identifier who is publishing its AS4 communication point (of the Connector linked to it).
- DocumentTypeIdentifier: Canonical evidence type.
- ProcessIdentifier: Orchestration type (request/response).
- AS4 endpoint: AS4 service endpoint URL.
- Certificate: The X.509 certificate of the AS4 server, used to encrypt the transmitted data for this specific participant.
The information described above is managed by the SML/DNS and SMP components and is used by the Connector when working with the phase4 implementation of AS4.
Focusing on the SML/DNS/SMP data retrieval, the process will take place according to the following features:
- SSL/TLS communication is mandatory.
- Response signature validation is mandatory.
- The communication between SMP and SML requires the usage of a client certificate.
The service metadata lookup will be performed as a step prior to the AS4 message exchange. Therefore, the participant IDs and other related information must be known by the Connector in advance.
Supported interaction patterns
Interaction patterns define the flow of data through the Connector and the intercommunication between the different components. Each pattern exchanges certain types of messages, and the incoming/outgoing information will depend on the processes occurring in the external components [3].
The Connector currently supports three interaction patterns:
- Intermediation (IM) pattern
- Asynchronous communication between the Connector and final participant (DE or DO).
- Data Owner endpoint must be known by the Data Transferor.
- Since the communication is synchronous, the Data Requestor does not need to know the identifier and endpoint of the Data Evaluator.
- User supported intermediation (USI) pattern
- Asynchronous communication between the Connector and final participant (DE or DO).
- Data Owner endpoint must be known by the Data Transferor.
- Since the communication is asynchronous, the Data Evaluator endpoint must be known by the Data Requestor. In addition, the Data Evaluator identifier is recovered from the request, since it is not sent in the response from the Data Transferor.
- Subscription and Notification (S&N) pattern
- Asynchronous communication between the Connector and final participant (DE or DO).
- Data Owner endpoint must be known by the Data Transferor.
- Since the communication is asynchronous, the Data Evaluator endpoint must be known by the Data Requestor. In addition, the Data Evaluator identifier is recovered from the request, since it is not sent in the response from the Data Transferor.
Most of the specific behaviour of each interaction pattern is independent of the Connector itself, as the Connector component is just designed to exchange messages and the main differences between the patterns take place in the external components such as the Data Evaluator and the Data Owner.
Additionally, the it2 connector offers a backwards compatibility feature for the IM pattern of it1. It can handle old messaging structure so implementation for it1 will be fully compatible with the it2 connector. In it1 IM pattern worked as a synchronous communication, this backwards compatibility also works with synchronous communication.
Connector roles
A Connector instance can play two different roles:
- Data Requestor (DR)
- Data Transferor (DT)
No configuration is needed to differentiate the roles, it only depends on the usage, i.e., the behaviour will be according to the messages sent.
Also, in a functional scenario the SMP data will determine which Connector is playing the DR or DT role.
AS4 implementations
The message exchange is built on the AS4 protocol, which is an open standard for secure, payload-agnostic business-to-business document exchange via web services. Secure document exchange is governed by WS-Security aspects, including XML Encryption and XML Digital Signatures.
Phase4
- Main features
- It is a generic AS4 solution.
- It can be integrated in basically any Servlet-based application server.
- It can easily be used with Peppol.
- It can be used with other Dynamic Discovery solutions.
- It supports a high degree of customization.
- It is not limited to the CEF/e-SENS profile.
- Implementation
- The Connector implements phase4 as a gateway to perform the AS4 message exchange.
All necessary configuration parameters are provided by the properties file of the Connector.
Error handling
Since the Connector performs multiple communications between different external components and some data and structure validations are performed, the Connector needs to monitor all failure points and be able to identify them in order to build the corresponding messages and warnings to inform each external component. When an error happens, the corresponding component creates an error message with the information about the error to be sent back to the entity that sent the failed message.
Kafka messages
Within the data flow and message exchange, there are many key points where it is important to know how the data is being managed, as well as identifying intermediate errors and unhandled system states. In this respect, the Connector can send messages to a Kafka server to track the data flow and trace the state of the system at certain points.
This feature is an advantage from a technical and business point of view, as the Connector performs the message exchange transparently to the other components.
It should be noted that the messages sent to the Kafka server are hardcoded, it is not a parameterizable feature, so any enhancements must be hardcoded again and deployed. It has been developed in such a way because the necessity of a Kafka server is not expected outside the DE4A project. In a real scenario, an alternative way of collecting logs should be implemented.
Message types
The Connector implements a Kafka message producer through the de4a-kafka-client library of the de4a-commons package. This producer provides several types of messages or severity levels:
- Success
- Info
- Warn
- Error
- Fatal error
Those message categories can be easily used to specify the severity level of the message sent to the Kafka server to track and identify them.
List of messages
The messages currently sent from the Connector to the Kafka server are as follows:
Services – (Info level)
- RequestTransferEvidenceIM message received - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluator:{2}, DataOwner:{3} - RequestTransferEvidenceUSI message received - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluator:{2}, DataOwner:{3} - RequestTransferEvidenceUSIDT message received - RequestId:
{0} - RequestLookupRoutingInformation message received - CanonicalEvidenceType:
{0}, CountryCode:{1}, DataOwnerId:{2} - Sending request to IDK - URL:
{0} - Looking for Data Owner address - DataOwnerId:
{0}
Client – (Info level)
- Requesting to SMP - ParticipantId:
{0}, DocumentTypeId:{1}, MessageType:{2} - Sending RequestForwardEvidence to the Data Evaluator - RequestId:
{0}, DataEvaluatorId:{1}, DataOwnerId:{2}, Endpoint: {3} - Sending RequestExtractEvidence IM to the Data Owner - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluatorId:{2}, DataOwnerId:{3}, Endpoint:{4} - Sending RequestExtractEvidence USI to the Data Owner - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluatorId:{2}, DataOwnerId:{3}, Endpoint:{4}
AS4 – (Info level)
- Sending request message via AS4 gateway - DataEvaluatorId:
{0}, DataOwnerId:{1}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{2} - Sending response message via AS4 gateway - DataEvaluatorId:
{0}, Message tag:{1}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{2} - Processing the request received via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0} - Processing the response received via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0}
Errors – (Error level)
- The corresponding request to the received response is not found on database - RequestId:
{0} - RequestForwardEvidence has not been sent, unknown Data Evaluator endpoint - RequestId:
{0}, DataEvaluatorId:{1} - RequestTransferEvidence not found on AS4 incoming message
- Error processing incoming message from AS4 gateway
- Error building URI from Data Evaluator endpoint:
{0} - Error sending message to Data Requestor via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0} - Data Owner address not found - DataOwnerId:
{0}
[1] The {x} symbols are placeholders for dynamic text to be logged.