Difference between revisions of "DE4A Connector"
(→Installation and configuration: Link added) |
|||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
The Connector project includes some utilities that allow the data processing and internal tools to perform all the Connector tasks. Those utilities are within the Connector project as a module called ''de4a-commons.'' | The Connector project includes some utilities that allow the data processing and internal tools to perform all the Connector tasks. Those utilities are within the Connector project as a module called ''de4a-commons.'' | ||
| − | ==Installation and configuration== | + | ==[[Installation and configuration guide|Installation and configuration]]== |
===Installation=== | ===Installation=== | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 23 February 2022
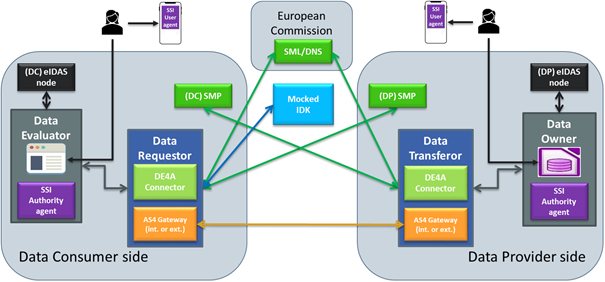
The DE4A Connector is a technical proxy that allows the final participants (DE or DO) to send requests for evidence or responses to other final participants over an eDelivery communication environment. In addition, to handle the message exchange process, the Connector is responsible for obtaining the message routing information, by exchanging information with external components such as the IDK, the SML/DNS or the SMP.
To do so, it provides a common interface to DEs and DOs, making the complexity of the system transparent to the final participants and integration easier.
The Connector component provides the AS4 Gateway functionality, so it can assume both the role of Data Requestor and Data Transferor. This first approach makes the Connector a stand-alone web application that can be deployed on any suitable application server. As an alternative, the Connector can make used of an external AS4 Gateway to provide the message exchange feature, in which case two components should be deployed: the DE4A Connector along with the chosen AS4 Gateway (i.e. Domibus).
The security and integrity of messages, as well as the unique identification of the participants involved, are the cornerstones of the Connector component.
Functionalities provided
The main purpose of the DE4A Connector is sending and receiving of evidence requests and their responses. The message exchange process is described in the DE4A deliverables D2.4 Project Start Architecture and D5.3 Initial technical design of interfaces.
Routing information lookup
The Connector is responsible for obtaining the Data Provider information from the IDK. It exposes a REST API /lookupRoutingInformation to get information about the Data Owners that provide a specific Canonical Evidence Type and further related information. That information is used to construct a request message to be sent through the Connector. Thus, the Data Evaluator is the only consumer of the mentioned API method.
Dynamic discovery of Services
In order for the Connector to be able to send a message to the corresponding endpoint, the eDelivery dynamic discovery mode of operation is used. This operation mode is based on the use of the SML/DNS and SMP components of the eDelivery infrastructure. The main elements stored in the SML/DNS and SMPs for this purpose are the following:
- ParticipantIdentifier: The Data Owner/Data Evaluator identifier who is publishing its AS4 communication point (of the Connector linked to it).
- DocumentTypeIdentifier: Canonical evidence type.
- ProcessIdentifier: Orchestration type (request/response).
- AS4 endpoint: AS4 service endpoint URL.
- Certificate: The X.509 certificate of the AS4 server, used to encrypt the transmitted data for this specific participant.
The information described above is managed by the SML/DNS and SMP components and is used by the Connector when working with the phase4 implementation of AS4. In cases where the Connector runs with external AS4 implementations such as Domibus, the end-to-end AS4 communication will be handled by the configuration of that external platform.
Focusing on the SML/DNS/SMP data retrieval, the process will take place according to the following features:
- SSL/TLS communication is mandatory.
- Response signature validation is mandatory.
- The communication between SMP and SML requires the usage of a client certificate.
The service metadata lookup will be performed as a step prior to the AS4 message exchange. Therefore, the participant IDs and other related information must be known by the Connector in advance.
Supported interaction patterns
Interaction patterns define the flow of data through the Connector and the intercommunication between the different components. Each pattern exchanges certain types of messages, and the incoming/outgoing information will depend on the processes occurring in the external components [3].
The Connector currently supports two interaction patterns:
- Intermediation (IM) pattern
- Synchronous communication between the Connector and final participant (DE or DO).
- Data Owner endpoint must be known by the Data Transferor.
- Since the communication is synchronous, the Data Requestor does not need to know the identifier and endpoint of the Data Evaluator.
- User supported intermediation (USI) pattern
- Asynchronous communication between the Connector and final participant (DE or DO).
- Data Owner endpoint must be known by the Data Transferor.
- Since the communication is asynchronous, the Data Evaluator endpoint must be known by the Data Requestor. In addition, the Data Evaluator identifier is recovered from the request, since it is not sent in the response from the Data Transferor.
Most of the specific behaviour of each interaction pattern is independent of the Connector itself, as the Connector component is just designed to exchange messages and the main differences between the patterns take place in the external components such as the Data Evaluator and the Data Owner.
Connector roles
A Connector instance can play two different roles:
- Data Requestor (DR)
- Data Transferor (DT)
No configuration is needed to differentiate the roles, it only depends on the usage, i.e., the behaviour will be according to the messages sent.
Also, in a functional scenario the SMP data will determine which Connector is playing the DR or DT role.
AS4 implementations
The message exchange is built on the AS4 protocol, which is an open standard for secure, payload-agnostic business-to-business document exchange via web services. Secure document exchange is governed by WS-Security aspects, including XML Encryption and XML Digital Signatures. There are many implementations of AS4, but the Connector currently implements phase4 and Domibus.
Phase4
- Main features
- It is a generic AS4 solution.
- It can be integrated in basically any Servlet-based application server.
- It can easily be used with Peppol.
- It can be used with other Dynamic Discovery solutions.
- It supports a high degree of customization.
- It is not limited to the CEF/e-SENS profile.
- Implementation
- The Connector implements phase4 as a gateway to perform the AS4 message exchange.
All necessary configuration parameters are provided by the properties file of the Connector.
Domibus
- Main features
- It ensures interoperable, secure and reliable data exchange.
- It is maintained by the European Commission.
- It manages the participants’ information and the end-to-end communication parameters.
- It is conceived as an eDelivery Access Point (external platform).
- Implementation
- The Connector implements Domibus as a gateway to send and receive messages to and from the Domibus access point.
Most of the configuration needed is on the Domibus service side.
Error handling
Since the Connector performs multiple communications between different external components and some data and structure validations are performed, the Connector needs to monitor all failure points and be able to identify them in order to build the corresponding messages and warnings to inform each external component. When an error happens, the corresponding component creates an error message with the information about the error to be sent back to the entity that sent the failed message.
Kafka messages
Within the data flow and message exchange, there are many key points where it is important to know how the data is being managed, as well as identifying intermediate errors and unhandled system states. In this respect, the Connector can send messages to a Kafka server to track the data flow and trace the state of the system at certain points.
This feature is an advantage from a technical and business point of view, as the Connector performs the message exchange transparently to the other components.
It should be noted that the messages sent to the Kafka server are hardcoded, it is not a parameterizable feature, so any enhancements must be hardcoded again and deployed. It has been developed in such a way because the necessity of a Kafka server is not expected outside the DE4A project. In a real scenario, an alternative way of collecting logs should be implemented.
Message types
The Connector implements a Kafka message producer through the de4a-kafka-client library of the de4a-commons package. This producer provides several types of messages or severity levels:
- Success
- Info
- Warn
- Error
- Fatal error
Those message categories can be easily used to specify the severity level of the message sent to the Kafka server to track and identify them.
List of messages
The messages currently sent from the Connector to the Kafka server are as follows:
Services – (Info level)
- RequestTransferEvidenceIM message received - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluator:{2}, DataOwner:{3} - RequestTransferEvidenceUSI message received - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluator:{2}, DataOwner:{3} - RequestTransferEvidenceUSIDT message received - RequestId:
{0} - RequestLookupRoutingInformation message received - CanonicalEvidenceType:
{0}, CountryCode:{1}, DataOwnerId:{2} - Sending request to IDK - URL:
{0} - Looking for Data Owner address - DataOwnerId:
{0}
Client – (Info level)
- Requesting to SMP - ParticipantId:
{0}, DocumentTypeId:{1}, MessageType:{2} - Sending RequestForwardEvidence to the Data Evaluator - RequestId:
{0}, DataEvaluatorId:{1}, DataOwnerId:{2}, Endpoint: {3} - Sending RequestExtractEvidence IM to the Data Owner - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluatorId:{2}, DataOwnerId:{3}, Endpoint:{4} - Sending RequestExtractEvidence USI to the Data Owner - RequestId:
{0}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{1}, DataEvaluatorId:{2}, DataOwnerId:{3}, Endpoint:{4}
AS4 – (Info level)
- Sending request message via AS4 gateway - DataEvaluatorId:
{0}, DataOwnerId:{1}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{2} - Sending response message via AS4 gateway - DataEvaluatorId:
{0}, Message tag:{1}, CanonicalEvidenceType:{2} - Processing the request received via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0} - Processing the response received via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0}
Errors – (Error level)
- The corresponding request to the received response is not found on database - RequestId:
{0} - RequestForwardEvidence has not been sent, unknown Data Evaluator endpoint - RequestId:
{0}, DataEvaluatorId:{1} - RequestTransferEvidence not found on AS4 incoming message
- Error processing incoming message from AS4 gateway
- Error building URI from Data Evaluator endpoint:
{0} - Error sending message to Data Requestor via AS4 gateway - RequestId:
{0} - Data Owner address not found - DataOwnerId:
{0}
[1] The {x} symbols are placeholders for dynamic text to be logged.
Data management
The Connector stores and manages certain information such as DE endpoints (not to be confused with SMP endpoints), DO endpoints, certain request records for asynchronous response matching, etc. All this data and where to find it is described in the following subsections.
Data Owner addresses
Once each Data Owner is publishing his Connector service information on the SMP, the request will arrive to that Connector service configured on the SMP (via the AS4 Gateway), and considering that one Connector could be serving to multiples DOs, this Connector has to know the addressing (base endpoint, without path name) information related to a specific participant identifier (e.g. iso6523-actorid-upis::9999:egov) to send forward the request to the corresponding Data Owner, so due to that, the Connector maintains a table, named owner_addresses, with two columns:
- AgentUrn: participant identifier in the DE4A format, e.g., iso6523-actorid-upis::9999:ess2833002e – see the “DE4A Policy for use of identifiers” for further information about the participant identifiers policy.
- Endpoint: base endpoint URL of the Data Owner who is exposing the service
/requestExtractEvidence
The information above will be used by a Connector playing the Transferor role when the RequestExtractEvidence message is being sent.
Security
The message exchange performed by the Connector has been conceived to ensure different security aspects as:
- Authenticity: ensures the identity of the participant entities and any common component involved in the message exchange. It is achieved through the participant identifiers definition, eDelivery specification and AS4 implementations.
- Integrity: refers to the accuracy and completeness of data. Security controls focused on integrity are used to prevent data from being modified or misused by an unauthorized party, provided by the WS-security and XML message signature.
- Confidentiality: data confidentiality at message level could be achieved by taking advantage of WS-Security encryption feature in User messages. This message encryption is performed via asymmetric keys: the sender of the message encrypts with the public key of the recipient, so the message can only be decrypted by the recipient, who owns the private key. Those keys should be configured either in the Connector in case of phase4 or in any external AS4 gateway.
Communications
The Connector creates a secure context to establish in/outgoing connections with external components.
The main elements for such communication securitisations are:
- Private key: private part of private-public key pair used in the TLS handshake between your server and the connecting clients. This private key must be configured in the Connector properties in order to create the secure context as well in the web server, in the case of reverse proxy or any similar structure. The keys configured on each component are generated under the DE4A management.
- Truststore: used for the storage of certificates from the trusted Certificate Authority (CA), which is used in the verification of the certificate provided by the server in an SSL connection. The Connector provides a default truststore which allows to trust on certificates generated under the main DE4A CA.
HTTP Proxy mode
Sometimes, the environments have certain communication structure where the outgoing connections must be performed through an HTTP proxy server. The Connector provides de functionality and proper configuration to perform the communications via an HTTP proxy server.
Message cryptographic protection
The Connector messages exchange can be separated into:
REST APIs messages
Once the SSL connection is established, all the data exchanged through it, will be encrypted on transport level based on the SSL context configuration settled, either managed by a reverse proxy on the server environment or configuring the proper application properties.
AS4 messages
- Phase4: internally the message is encrypted using a specific keystore configuration only used for this purpose; also the cross-gateways communications are additionally encrypted over the HTTPS secure protocol.
- Domibus: the bridge between the Connector and Domibus service is securitized by encrypting the messages content as well as signing the message, in accordance with the AS4 policies and the transport protocol used. It implements a Spring web service gateway using WS-security at SOAP message exchange level. About the message exchange between Domibus instances, it is handled internally by the platform.
Message validation
Message validation is performed at different stages of the Connector data flow, from message structure compliance to content integrity.
Schema validation
All the messages produced and consumed by the Connector are performing an XML Schema validation once it is received or sent out. This validation is done by the object conversion library that keeps the schema model including all the structure and content constraints.
Signature validation
As well as the XML Schema validation, the Connector performs validations to ensure the content and reliability on certain phases of the message exchange process:
- Services metadata querying
- In the SMP data exchange a message signature validation is being performed to maintain the content reliability. This validation consists of verifying the embedded signature on the message against the trust certificate configured in the Connector for that purpose.
The signature of incoming AS4 messages is verified against the central AS4 Gateway CA globally used in DE4A project, internally validated by the implementation libraries that handle the reception and delivery.
Technology used
System core architecture
The Connector works as standalone application that runs different web services according to the RESTful API architecture principles. The application is built with the following tools:
- Spring Framework version 5.x.
- Java 11
- Apache HTTP Client 4.x
In addition to the core architecture, the XML Schemas defined to model the exchanged information, data constraints, interfaces, etc. are also important. All this is part of the Connector core through the de4a-commons library, which contains the above-mentioned model as well as utilities and conversion tools.
- Author: DE4A (WP5)
- Repository: https://github.com/de4a-wp5/de4a-commons
Third party libraries
As part of the bunch of libraries used by the Connector there are some of the related with the core features and which represent a starting point for the functionalities provided by the Connector.
TOOP Connector
The TOOP Connector is a set of shared utility functions used in the Connector to perform common tasks that are required for a safe and interoperable data exchange. In the initial iteration the latest version of the TOOP Connector technical components were reused mainly for the usage of the built-in phase4 AS4 Gateway. Other elements of the TOOP Connector are currently ignored.
- Author: TOOP Project
- Repository: https://github.com/de4a-wp5/toop-connector-ng
ph-oton libraries
Set of Java libraries to build Java web applications.
- Author: Philip Helger (phax)
- Repository: https://github.com/phax/ph-oton
Peppol commons libraries
They include the SMP client library used by the Access Points to retrieve service metadata. This library supports the Peppol SMP specification, the OASIS BDXR SMP v1 and OASIS BDXR SMP v2 specification. This project uses Apache HTTP client to perform the REST lookups on foreign SMPs.
- Author: Philip Helger (phax)
- Repository: https://github.com/phax/peppol-commons
Data management
To manage the model and the data stored by the Connector the following technologies are used:
- JPA: The Java Persistence API is a specification of Java. It is used to persist data between Java object and relational database. JPA acts as a bridge between object-oriented domain models and relational database systems. As JPA is just a specification, it does not perform any operation by itself.
- Hibernate: An object–relational mapping tool for the Java programming language. It provides a framework for mapping an object-oriented domain model to a relational database. Hibernate handles object–relational impedance mismatch problems by replacing direct, persistent database accesses with high-level object handling functions.
Utilities libraries
The project uses several libraries and utilities to process and transform the data. They can be divided according to their nature:
- Commercial libraries
To perform common and non-business operations on web and data exchange projects, the Connector uses different commercial solutions, also all the libraries embedded in the Java development kit.
- In-house solutions
The Connector project includes some utilities that allow the data processing and internal tools to perform all the Connector tasks. Those utilities are within the Connector project as a module called de4a-commons.
Installation and configuration
Installation
As a prerequisite to build the Connector is to have at least Java 11 and Apache Maven 3.6 or later installed.
You should be able to compile entire packages from the parent POM file:
mvn clean install
It is also possible to compile each package separately by browsing to the folder and running the command above.
Package
The compilation process will be packaging the project into a .war file located on /target/ path, which should be deployable on any applications server. If you compile the parent pom, the IDK and Connector target paths will be created with their corresponding war files.
- de4a-commons
de4a-commons project is now on maven central OSS Sonatype repository
- Toop version v2.1.2-SNAPSHOT
Due to the lastest changes on de4a-commons Toop-connector-ng version should be 2.1.2-SNAPSHOT, so you may need to add following repo server on your maven settings
https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/
Connector configuration guide
For a correct configuration of the Connector, three main property files must be considered:
application.properties: main system configurationphase4.properties: AS4 gateway configurationslog4j2.xml: logging configuration
Bellow, a working example of the application.properties file:
# Database properties
database.datasourceConf.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
database.datasourceConf.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
database.datasourceConf.username=sa
database.datasourceConf.password=password
database.datasourceConf.initializationMode=always
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.dialectPlatform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.ddlauto=create-drop
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.generateddl=true
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.namingStrategy=org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.showSql=true
database.datasourceConf.jpaHibernate.formatSql=true
# H2 in-memory database console port (default 21080)
h2.console.port=21080
# i18n properties
spring.messages.basename=messages/messages
spring.messages.default_locale=en
# Spring allowing override beans
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
# Charset encoding
server.servlet.encoding.charset=UTF-8
server.servlet.encoding.enabled=true
server.servlet.encoding.force=true
# SSL context enabled (true|false)
ssl.context.enabled=false
# SSL configuration (optional when ssl.context.enabled is false, otherwise, it must be configured)
#ssl.keystore.type=
#ssl.keystore.path=
#ssl.keystore.password=
#ssl.truststore.path=
#ssl.truststore.password=
# Global flags for initializer
global.debug = true
global.production = false
# Instance name for logging
global.instancename = dev-from-ide
# DE4A Kafka settings
de4a.kafka.enabled=true
# Enables the standard logging separately of the Kafka messages. It is necessary for print metrics messages - (default: true)
de4a.kafka.logging.enabled=true
# Enables Kafka connection via HTTP (Only enable HTTP mode if outbound TCP connections are blocked from your internal network)
de4a.kafka.http.enabled=false
# Kafka server address (Eg.: de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu:9092)
de4a.kafka.url=de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu:9092
# Uncomment the following property and remove the above one if HTTP mode is enabled
# de4a.kafka.url=https://de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu
# Establish a topic on kafka tracker - Pattern: de4a-<country-code>-<partner-name> - Eg.: de4a-se-egovlab - (default: de4a-connector)
de4a.kafka.topic=de4a-connector
# Logging metrics messages prefix - Default: DE4A METRICS
log.metrics.prefix=DE4A METRICS
# toop legacy kafka properties (Do not touch)
toop.tracker.enabled = false
# DSD base URL (Do not modify)
toop.dsd.service.baseurl = http://dsd.dev.exchange.toop.eu
# What AS4 implementation to use?
toop.mem.implementation = phase4
# Our AS4 sending AP endpoint (holodeck)
#toop.mem.as4.endpoint = http://localhost:8083/tc-webapp/as4
# Domibus server endpoint
# domibus.endpoint=
# SMP Client configuration stuff - Do not modify (default values)
smpclient.truststore.type = JKS
smpclient.truststore.path = truststore/de4a-truststore-test-smp-pw-de4a.jks
smpclient.truststore.password = de4a
# Spring As4 gateway implementation bean(provided: phase4GatewayClient and domibusGatewayClient).Implements eu.toop.as4.client.As4GatewayInterface
as4.gateway.implementation.bean=phase4GatewayClient
# External endpoints
# SMP endpoint Eg.: https://de4a-smp.egovlab.eu/
smp.endpoint=
# IDK endpoint Eg.: https://de4a-dev-idk.egovlab.eu/
idk.endpoint=
# IM response timeout
as4.timeout.miliseconds=30000
# Properties to create the http client connection through a proxy (optional)
#http.proxy.enabled=
#http.proxy.address=
#http.proxy.port=
#http.proxy.non-proxy=
#http.proxyUsername=
#http.proxyPassword=
# Required renamed proxy configuration for BDXRClient (if is needed, only uncomment)
#http.proxyHost=${http.proxy.address}
#http.proxyPort=${http.proxy.port}
#http.nonProxyHosts=${http.proxy.non-proxy}
From now on, we will explain the main and most critical configuration.
Database properties
Regarding database configuration and structure, the component creates an in-memory database through an H2 DB Engine, which will be created and deleted on each execution.
- Datasource parameters
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password=password spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
On the previous properties you also can specify any driver o connection configuration in order to stablish the connection to any database engine.
- H2 in-memory database console
In order to access and manage information stored, until an external environment is created, the Connector expose H2 server engine console on the port defined by the property:
h2.console.port=21080
By default, even if you do not define the property (non-empty), port will be 21080, so you will be able to access through the following direction pattern:
http://<host-endpoint>:<portH2Console>
SSL Context (not for AS4) application.properties
You can configure secure HTTP connections from the Connector by setting the following property to true:
# SSL context enabled (true|false) ssl.context.enabled=true
In this case you should properly configure the following properties in order to create an SSL context for HTTP communications:
- SSL configuration (optional when ssl.context.enables is false)
ssl.keystore.type= #(JKS|PKCS12) ssl.keystore.path= #(Path to keystore where signing private key are included) ssl.keystore.password= #(Private key password) ssl.truststore.path= #(JKS truststore) ssl.truststore.password= #(Truststore password)
In the case that you disabled the SSL context property, you should configure the corresponding JVM parameters to specify the truststore, keystore, etc. or the further actions depending of your environment configuration.
Kafka configuration application.properties
To send log messages to a Kafka server, configure the following parameters:
# DE4A Kafka settings de4a.kafka.enabled=true # Enables the standard logging separately of the Kafka messages. It is necessary for print metrics messages - (default: true) de4a.kafka.logging.enabled=true # Enables Kafka connection via HTTP (Only enable HTTP mode if outbound TCP connections are blocked from your internal network) de4a.kafka.http.enabled=false # Kafka server address (Eg.: de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu:9092) de4a.kafka.url=de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu:9092 # Uncomment the following property and remove the above one if HTTP mode is enabled # de4a.kafka.url=https://de4a-dev-kafka.egovlab.eu # toop legacy kafka properties (Do not touch) toop.tracker.enabled = false
IMPORTANT - If your server has no access to external domains, the HTTP Kafka and proxy configuration should be enabled. To enable HTTP Kafka log producer, you only need to set the property to true de4a.kafka.http.enabled=true - Also configure the proper endpoint in order to use HTTP connections.
An important setting is to set the de4a.kafka.topic to something that distinguishes your service from all the others. A good naming convention for your topic would be de4a-<two letter country code>-<pilot/partner acronym>.
It is important to mention the property de4a.kafka.logging.enabled, used to enable the file log printing for each Kafka message sent, that property could be enabled even when the de4a.kafka.enabled=false, just for write the log at the different appenders configured in the log4j2 configuration file.
SMP properties application.properties
To establish which SMP server will provide the Connector with metadata services, the following properties must be used:
# SMP Client configuration stuff - Do not touch (default values) smpclient.truststore.type = JKS smpclient.truststore.path = truststore/de4a-truststore-test-smp-pw-de4a.jks smpclient.truststore.password = de4a .......... # External endpoints smp.endpoint= You can define there your SMP endpoint and truststore which will be used to validate the signature of the responses.
Do not modify, all consortium SMPs should be validated with the default truststore.
AS4 – phase4 configuration
# What AS4 implementation to use? toop.mem.implementation = phase4 .......... # Spring As4 gateway implementation bean(provided: phase4GatewayClient and domibusGatewayClient).Implements eu.toop.as4.client.As4GatewayInterface as4.gateway.implementation.bean=phase4GatewayClient .......... # Domibus server endpoint # domibus.endpoint=
The Connector includes two different gateways acting as interfaces to the AS4 outgoing messages, but on one hand the phase4 gateway uses the internal libraries phase4/TOOP to process the outgoing/incoming messages, meanwhile, the Domibus gateway needs to send the messages to an external platform which will take over the exchange role. In this case, it just needs to configure the following parameters to runs the Connector over the phase4 gateway.
# What AS4 implementation to use? toop.mem.implementation = phase4 .......... # Spring As4 gateway implementation bean(provided: phase4GatewayClient and domibusGatewayClient).Implements eu.toop.as4.client.As4GatewayInterface as4.gateway.implementation.bean=phase4GatewayClient
Also, all the concerns about phase4/TOOP versions are handled by the Connector itself, which is built using the corresponding versions regarding the compatibility and functionality.
AS4 – Domibus configuration
When configuring the Connector to run with the Domibus gateway it is important to align the party’s identifiers both in the Connector and in the Domibus PMode configuration [8] to allow the proper functioning.
- application.properties
.......... # Spring As4 gateway implementation bean (provided: phase4GatewayClient and domibusGatewayClient).Implements eu.toop.as4.client.As4GatewayInterface as4.gateway.implementation.bean=domibusGatewayClient ……… # Domibus properties domibus.endpoint=https://<domibus-host>/domibus/services/backend
- phase4.properties
# (string) - the from party ID to be used for outgoing messages. Previous versions need to use toop.mem.as4.tc.partyid - starting from RC3 this property is still used as a fallback) phase4.send.fromparty.id=egdovlab # (string) to party ID to be used for outgoing messages. Configure it in case of using Domibus without dynamic participant discovery or in the phase4 side in a mixed AS4 implementations phase4<->Domibus phase4.send.toparty.id=sgad # (string) - the AS4 To/PartyId/@type value. E.g. urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered phase4.send.toparty.id.type=urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered # (string) - the AS4 From/PartyId/@type value. E.g. urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered phase4.send.fromparty.id.type=urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered
In addition to the common configuration of phase4, the mentioned above is especially important to match with the configuration settled on the Domibus instance.
About the compatibility between the Connector and Domibus, it has been tested versions from 4.1.6 to the current (4.2.2).
Proxy properties
Some environments may require to perform proxy connections due to security policies or environment limitations. That is why the Connector allows to establish HTTP connections via proxy.
# Properties to create the HTTP client connection through a proxy (optional)
#http.proxy.enabled=
#http.proxy.address=
#http.proxy.port=
#http.proxy.non-proxy= ("|" delimiter)
#http.proxyUsername=
#http.proxyPassword=
# Required renamed proxy configuration for BDXRClient (if needed, only uncomment)
#http.proxyHost=${http.proxy.address}
#http.proxyPort=${http.proxy.port}
#http.nonProxyHosts=${http.proxy.non-proxy}
To disable proxy configuration, you can either comment the properties or set up enabled property to false: http.proxy.enabled=false
PLEASE NOTE that in case that you enabled the property (http.proxy.enabled=true) above you should uncomment and set up the rest of them. Also uncomment properties regarding to BDXRClient.
phase4 properties
Parameters used by the built-in Phase4 module of the Connector. Set up the properties above following the commented indications. Some of them are filled in to clarify the content -- Important to consider if each property is optional or not (check out the in-line comments).
# (string) - the absolute path to a local directory to store data phase4.datapath= # (boolean) - enable or disable HTTP debugging for AS4 transmissions. The default value is false. phase4.debug.http= # (boolean) - enable or disable debug logging for incoming AS4 transmissions. The default value is false. phase4.debug.incoming= # (string) - an optional absolute directory path where the incoming AS4 messages should be dumped to. Disabled by default. phase4.dump.incoming.path= # (string) - an optional absolute directory path where the outgoing AS4 messages should be dumped to. Disabled by default. phase4.dump.outgoing.path= # (string) - the from party ID to be used for outgoing messages. Previous versions need to use toop.mem.as4.tc.partyid - starting from RC3 this property is still used as a fallback) phase4.send.fromparty.id= # (string) to party ID to be used for outgoing messages. Configure it in case of using Domibus without dynamic participant discovery or in the phase4 side in a mixed AS4 implementations phase4<->Domibus phase4.send.toparty.id= # (string) - the AS4 To/PartyId/@type value. E.g. urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered phase4.send.toparty.id.type=urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered # (string) - the AS4 From/PartyId/@type value. E.g. urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered phase4.send.fromparty.id.type=urn:oasis:names:tc:ebcore:partyid-type:unregistered # (string) - an optional folder, where sent responses should be stored. If this property is not provided, they are not stored phase4.send.response.folder= # (string) - the type of the keystore (either "JKS" or "PKCS12" - case insensitive) - defaults to JKS. phase4.keystore.type= # (string) - the path to the keystore (can be classpath relative or an absolute file) phase4.keystore.path= # (string) - the password to access the keystore phase4.keystore.password= # (string) - the alias of the key in the keystore (may be case sensitive) phase4.keystore.key-alias= # (string) - the password to access the key in the keystore phase4.keystore.key-password= # (string) - the type of the truststore (either "JKS" or "PKCS12" - case insensitive) - defaults to JKS. phase4.truststore.type= # (string) - the path to the truststore (can be classpath relative or an absolute file) phase4.truststore.path= # (string) - the password to access the truststore phase4.truststore.password=
Logging configuration log4j2.xml
The configuration file bellow maintains the logging configuration where you can set the level of each appender, set up log file path, or even include more appenders or configuration. Important - to correctly configure the path of log file. By default it is a relative path to catalina.base (Tomcat server): ${sys:catalina.base}/logs/connector.log
<RollingFile name="rollingFile"
fileName="${sys:catalina.base}/logs/connector.log"
filePattern="${sys:catalina.base}/logs/history/connector.%d{dd-MMM}.log.gz"
ignoreExceptions="false">
<PatternLayout>
<Pattern>>[%date{ISO8601}][%-5level] %msg -- %location [%thread]%n</Pattern>
</PatternLayout>
<Policies>
<OnStartupTriggeringPolicy />
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="30 MB" />
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="5" />
</RollingFile>
<RollingFile name="metricsFile"
fileName="${sys:catalina.base}/logs/metrics-connector.log"
filePattern="${sys:catalina.base}/logs/history/metrics-connector.%d{dd-MMM}.log.gz"
ignoreExceptions="false">
<PatternLayout>
<Pattern>>$${ctx:metrics:-}[%date{ISO8601}][%-5level][$${ctx:logcode:-}][DE4A-CONNECTOR][$${ctx:origin:-}][$${ctx:destiny:-}] %msg -- %location [%thread]%n</Pattern>
</PatternLayout>
<Policies>
<OnStartupTriggeringPolicy />
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="30 MB" />
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="5" />
</RollingFile>
Two different log files are been generated, rollingFile include more technical and debuggin log lines, whereas metricsFile is composed by metrics messages specificied mostly at list of log messages.
Also, in the application.properties there is another property related with the logging.
# Logging metrics messages prefix - Default: DE4A METRICS log.metrics.prefix=DE4A METRICS
It is used to include a prefix on each logging line written by the Kafka logging that could be useful to parse and filter the lines with metrics information.
Starting up the Connector
Once you have all configuration parameters well configured (if not, check the logs to find out the problem), it is time to deploy the component into an applications server. Once you have deployed the war file or the docker image, there are several checks to ensure that the deployment was successful:
- Open Swagger UI browsing:
http://host:port/swagger-ui/
E.g.: UM Connector
- DE4A Connector index page will be at root path:
http://host:port/
E.g.: UM Connector
- The Connector will be able to process requests through the following interfaces:
/requestTransferEvidenceIM
/requestTransferEvidenceUSI
/lookupRoutingInformation
/requestTransferEvidenceUSIDT